Avro
Read and write Avro
Flow can read and write data using Avro.
To declare that a type should be read as CSV, add the lang.taxi.formats.AvroMessage annotation to a model:
import lang.taxi.formats.AvroMessage
@AvroMessage
closed model People {
name: Name
id: sId
email: Email?
phones: Phones[]
last_updated: LastUpdated
}When writing Avro, serialization order is important. Therefore, you should also specify the field order using an AvroField annotation:
import lang.taxi.formats.AvroMessage
import lang.taxi.formats.AvroField
@AvroMessage
closed model People {
@AvroField(ordinal = 0) name: Name
@AvroField(ordinal = 1) id: Id
@AvroField(ordinal = 2) email: Email?
@AvroField(ordinal = 3) phones: Phones[]
@AvroField(ordinal = 4) last_updated: LastUpdated
}Any requests or responses sent to/from systems where the model type has been annotated with @AvroMessage will be
serialized using Avro.
Add Taxi types to Avro
Just like all schemas in Flow, Taxi types are required to indicate how data is linked and relates between systems.
To add Taxi metadata to your Avro file, use the taxi.dataType attribute.
Here’s an example assigning a Taxi type name to a record / object:
{
"type": "record",
"namespace": "simple",
"name": "AddressBook",
// without this annotation, a type of simple.AddressBook would have
// been created, based off the namespace and name
"taxi.dataType": "com.example.AddressBook",
"fields": [
//... continues ...
]
}Or, to define a Taxi type for a field:
{
"type": "record",
"name": "Person",
"fields": [
{
"name": "name",
"type": "string",
"taxi.dataType": "foo.PersonName"
},
{
"name": "id",
"type": "int",
"taxi.dataType": "foo.PersonId"
}
// ... continues ...
]
}If a schema does not define / expose Taxi types for fields, Flow will assign them automatically.
For records, the namespace and name are used to infer the type name.
For fields, a type is created based off the field name, and the type, which defines the underling primitive type.
Add Avro projects to your workspace
Schemas declared in Avro can be added to your workspace by either editing your workspace file (normally workspace.conf),
or through the UI.
Use the workspace file
Local file projects
You can add Avro schemas that are present locally on the file system of the server by adding the following declaration to your workspace.conf file:
file {
projects=[
{
loader {
// All projects in {short-product-name} require a unique identifier
identifier {
id="com.hazelcast/avro-test/1.0.0"
name=avro-test
organisation="com.hazelcast"
unversionedId="com.hazelcast/avro-test"
uriSafeId="com.hazelcast:avro-test:1.0.0"
version="1.0.0"
}
// set the packageType to Avro
packageType=Avro
}
packageIdentifier {
name=avro-test
organisation="com.hazelcast"
version="1.0.0"
}
// The path on your local machine to the avro schema
path="/opt/resources/avro/addressBook.avsc"
}
]
}Git projects
You can add Avro schemas that are present within a Git repository by adding the following declaration to your workspace.conf file:
The Git repo is monitored, so any changes are pulled locally and automatically applied inside of Flow.
git {
repositories=[
{
branch=main
loader {
identifier {
id="com.avro.git/avro/1.2.3"
name=avro
organisation="com.avro.git"
unversionedId="com.avro.git/avro"
uriSafeId="com.avro.git:avro:1.2.3"
version="1.2.3"
}
packageType=Avro
}
name=test-project
// The path to the avro file within your Git repository
path="/addressBook.avsc"
// The url of your git repo
uri="https://gitlab.com/acme/my-avro-project.git"
}
]
}Use the UI
You can load Avro schemas into your workspace using the UI.
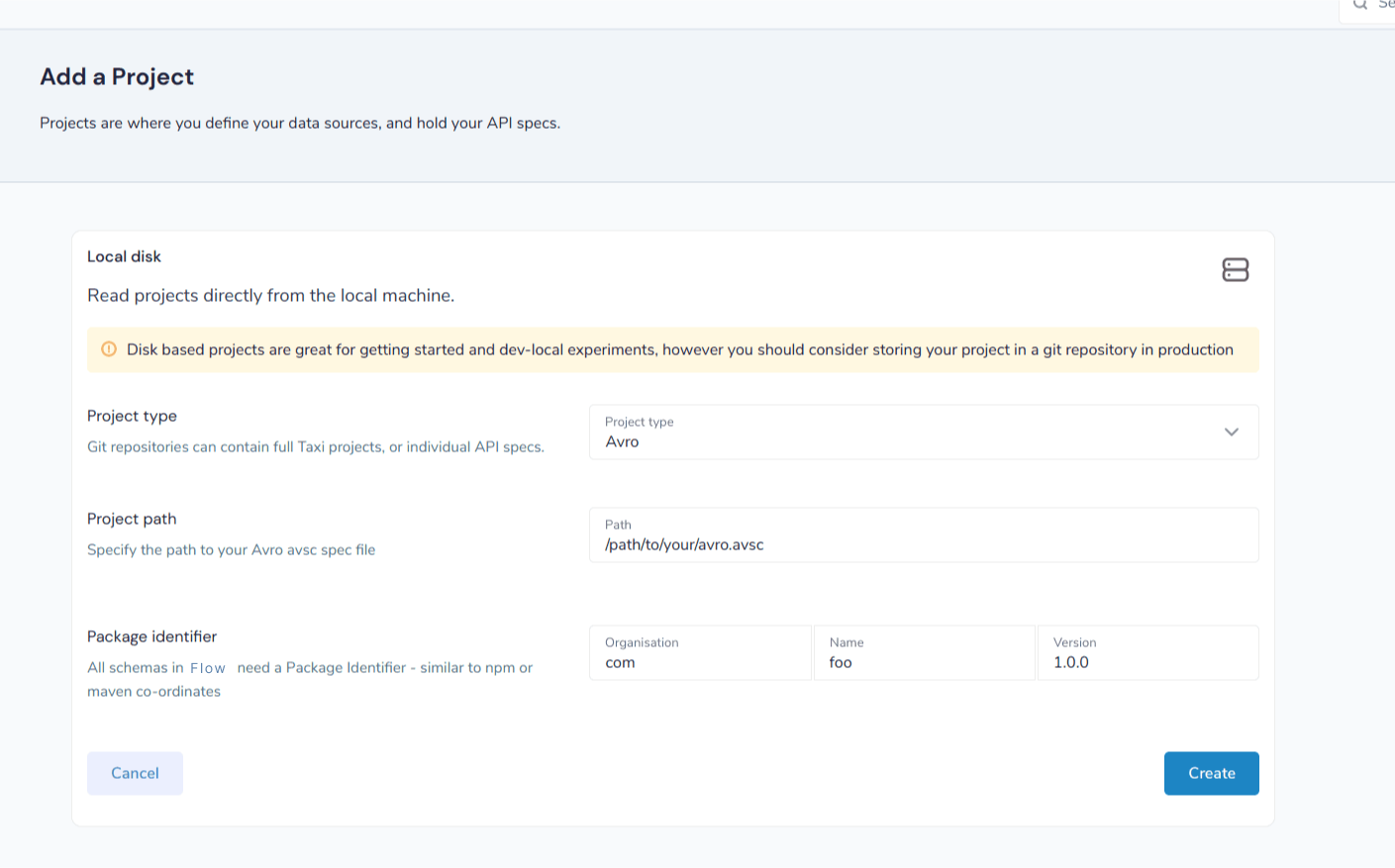
Start by navigating:
-
Projects > Add Project
-
Then select to add a project from either a Git Repo or Local disk
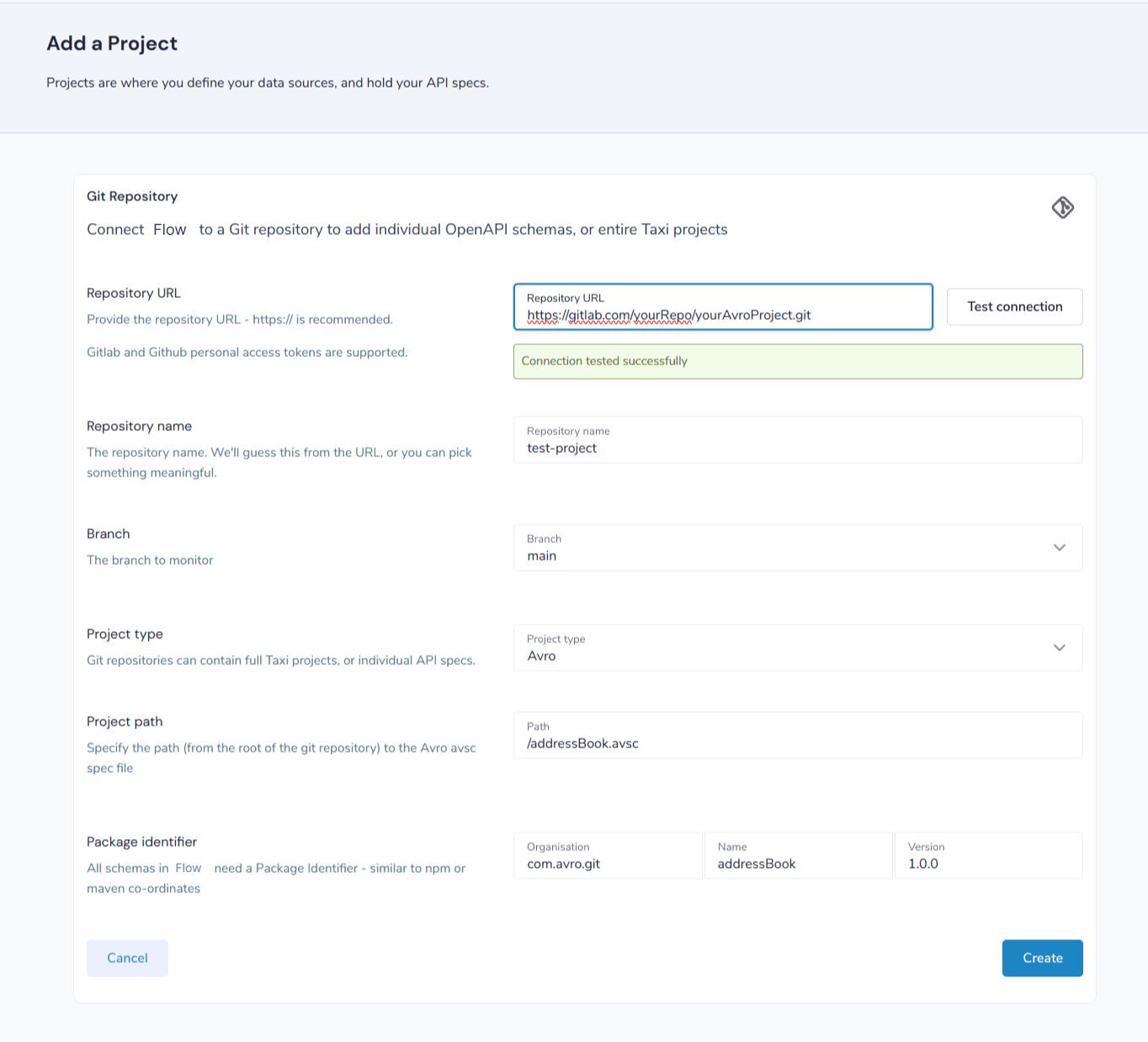
Add an Avro project from Git
This workflow lets you add a reference to an Avro schema that’s checked into a Git repository.
The Git repo is monitored, so any changes are pulled locally and automatically applied inside of Flow.
-
Provide the URL of the Git repository, and click Test Connection
-
If the test was successful, repository name and branch are populated for you
-
-
Set the project type to Avro
-
Set the path to the location of your Avro schema within the repo
-
Provide a unique package identifier for this Avro schema
Add an Avro project from a file
This workflow lets you add a reference to an Avro schema that’s already local on the server.
Any changes made to the file are automatically detected, and updated inside of Flow.
| 'Local' means local to the server. |
This workflow adds a reference to an Avro file that’s on the disk of the server.
It’s intended for developers who are running Flow in a container on their local machine.
This workflow isn’t intended for uploading an Avro schema to a remote server. Instead, use a Git repository
-
Set the project type to Avro
-
Provide the path on your local machine to where the Avro file is
-
Provide a unique package identifier for this Avro schema