Scripting
You can use the scripting feature of the Management Center to execute scripts on the cluster.
Before you Begin
Scripting is disabled by default, and you need to enable it in your cluster’s configuration. See the Toggle Scripting Support for details. The member list shows whether scripting is enabled or disabled for each member.
| Java 15 and newer versions do not come with a JavaScript engine. If you want to use JavaScript as a scripting language on a member with Java 15 and newer, the appropriate libraries should be placed in the classpath of that member. See the Enabling Scripting Languages section for more details. |
Scripting in JavaScript
To use this feature, click on the Scripting menu item on the left panel.
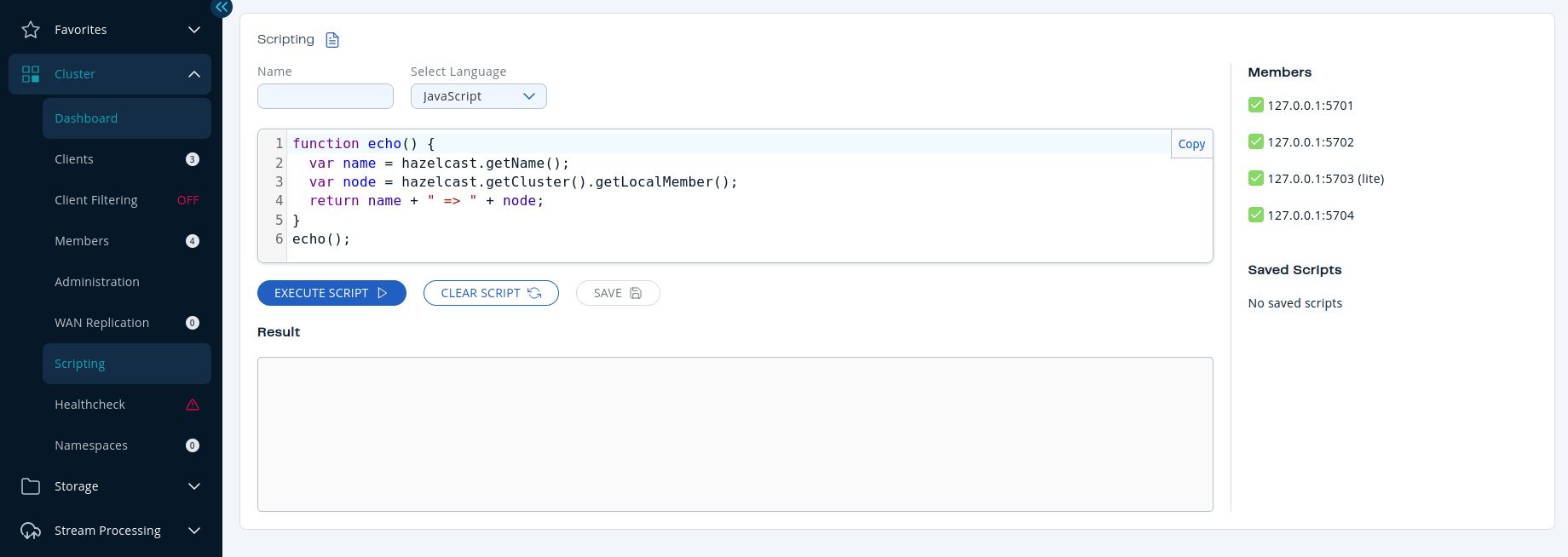
In this window, the left panel is the actual script code editor. The combo box located at the top part of the editor enables you to select a scripting language: currently, JavaScript, Ruby, Groovy and Python languages are supported. You can select the members on which the code will execute from the Members list shown on the right side of the screen. After you write your script and press the Execute button, you can see the execution result in the Result part of the window.
| To use the scripting languages other than JavaScript on a member, the libraries for those languages should be placed in the classpath of that member. See the Enabling Scripting Languages section for more details. |
There are Save and Delete buttons on the top right of the scripting editor. To save your scripts, press the Save button after you type a name for your script into the field next to this button. The scripts you saved are listed in the Saved Scripts part of the window, located at the bottom right of the page. Click on a saved script from this list to execute or edit it. If you want to remove a script that you wrote and saved before, select it from this list and press the Delete button.
In the scripting engine you have a HazelcastInstance bonded to a variable
named hazelcast. You can invoke any method that HazelcastInstance has via
the hazelcast variable. You can see an example usage for JavaScript below:
var name = hazelcast.getName();
var node = hazelcast.getCluster().getLocalMember();
var employees = hazelcast.getMap("employees");
employees.put("1","John Doe");
employees.get("1"); // will return "John Doe"Enabling Scripting Languages
Hazelcast members use the javax.script.ScriptEngineManager API for the execution of the script.
The JavaScript engine is available in most JVMs of versions older than 15 by default.
To use a scripting language on a member, you need to add the
corresponding scripting engine and all its transitive dependencies to the classpath of that member.
Here is an example of Maven configuration for several scripting engines:
<dependencies>
<!-- JavaScript -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.nashorn</groupId>
<artifactId>nashorn-core</artifactId>
<version>15.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Groovy -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<artifactId>groovy-jsr223</artifactId>
<version>3.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Ruby (JRuby) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mule.modules</groupId>
<artifactId>mule-module-scripting-jruby</artifactId>
<version>3.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Python (Jython) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.python</groupId>
<artifactId>jython-standalone</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>